Resistors
Resistors are passive devices that give you control over the currents and voltages that flow within a circuit. Electrical resistance describes how easy it is for electricity to flow through the circuit. By using a resistor, you can add resistance to the passage of an electric current, making it harder for electricity to flow through it.
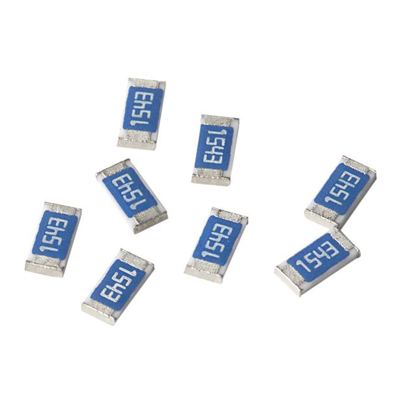
Most resistors are small devices that have colored stripes around them to indicate the resistor’s tolerance and resistance. They are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Digital electronics
- Measurement devices
- LED lights
- Air ventilation systems in cars
- Electric stoves
- Gas sensors
PUI Projections Unlimited stocks and distributes all types of electronic components, including various resistors for your application needs. Contact us today to learn more.
Types of Resistors
Some applications require a different amount of resistance or power, and some require a specific resistor material. For these reasons, there are a variety of resistors that are designed to meet the requirements of different applications.
Contact PUI Projections for Your Electronic Component Needs
We are an authorized distributor selling electronic components from manufacturers with a reputation for high quality. Our team has vast technical experience and can help you find the electronic component that you need for your application. We strive to always provide the best customer satisfaction.
To learn more about our resistors, contact us today or request a quote.